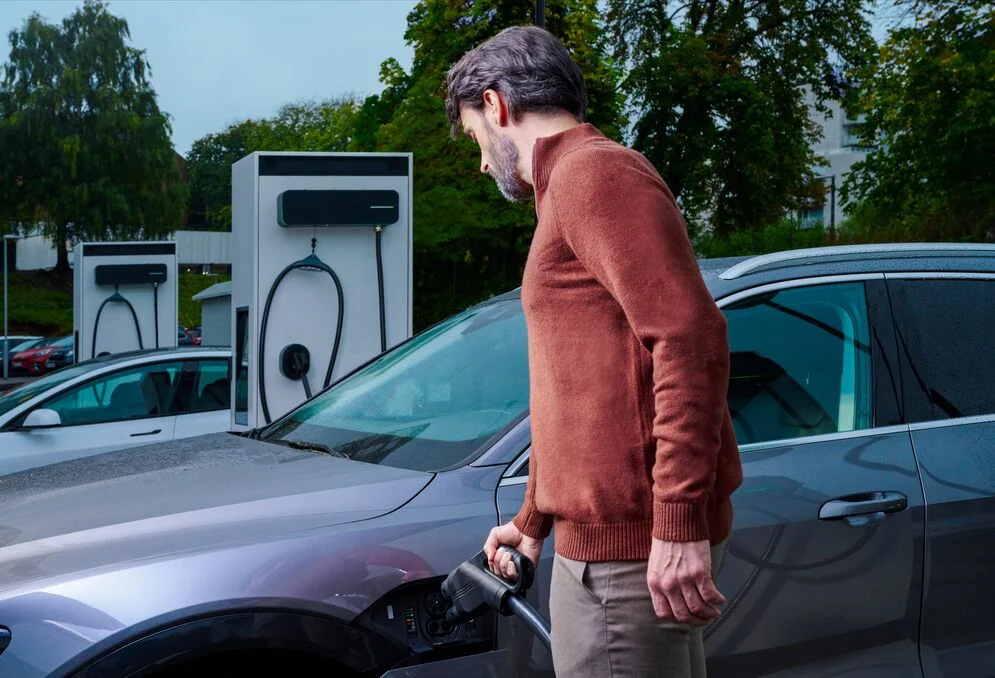

DC Fast Charger: A Rapidly Evolving Business OpportunityÂ
Refueling used to be a routine at gas stations. Now, with electric vehicles, drivers can charge anywhere they park, offering new opportunities for businesses. With rising EV sales, range anxiety remains a barrier, but strategically placed fast chargers can help overcome this.
As the EV industry grows, businesses have a chance to tap into the fast charging market. Many are exploring DC solutions to meet this demand.
Let’s dive into the technical side of DC charging technology.
What is DC Fast Charging?Â
DC fast charging, also known as Level 3 charging, is the fastest and most powerful option available. It delivers between 50 kW and 400 kW, adding up to 298 miles (480 km) of range in just one hour, depending on the vehicle and its specifications.
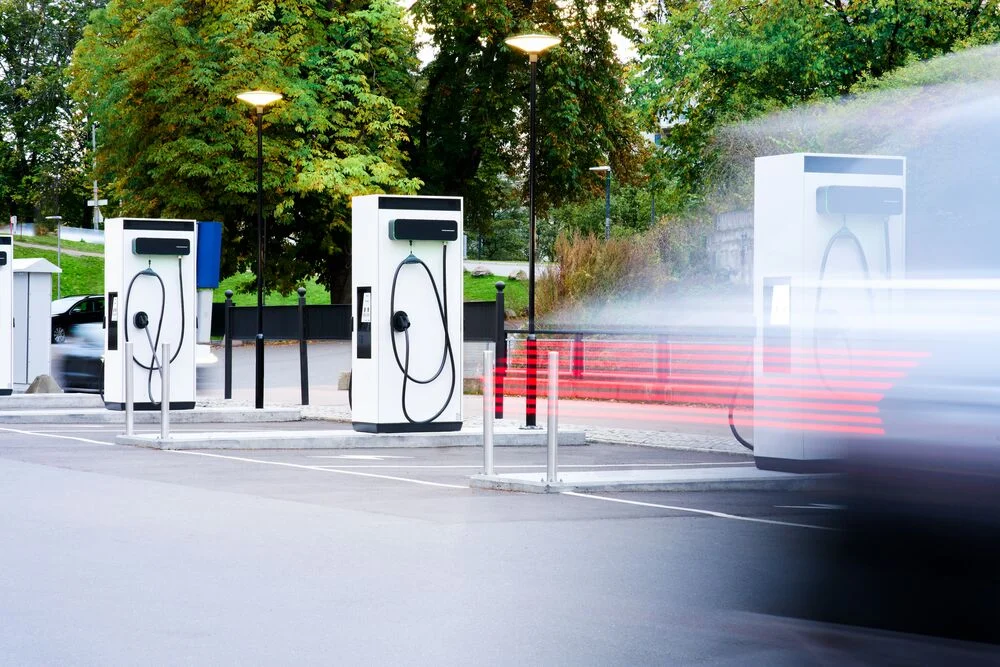

DC charging is much faster than AC, which typically takes hours. This makes it ideal for drivers who need a quick charge while on the go.
For example:
- DC fast-charging station: 17–52 minutes for a medium-sized EV.
- AC charging station: 1 hour 45 minutes to 6 hours for a medium-sized EV.
This difference can make a big impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty.

Why Is DC Charging Faster Than AC?
EV batteries store DC power, but the grid provides AC. AC must be converted to DC before it can be stored. In DC charging, this conversion happens within the station itself, not inside the vehicle. This results in faster charging times compared to AC charging.
You can read more about the differences between AC and DC here.
How Much Does a DC Charging Station Cost?Â
Compared to commercial AC stations, DC fast chargers require a significant investment. Costs depend on factors like the maximum power output, location, and installation complexity.

On average, a DC charging station costs around €50,000 per unit, excluding installation, which usually adds another 30–50% to the total cost.
DC Charging Station ArchitectureÂ
Understanding the footprint of a DC charging station is essential. There are two main types: standalone and split.
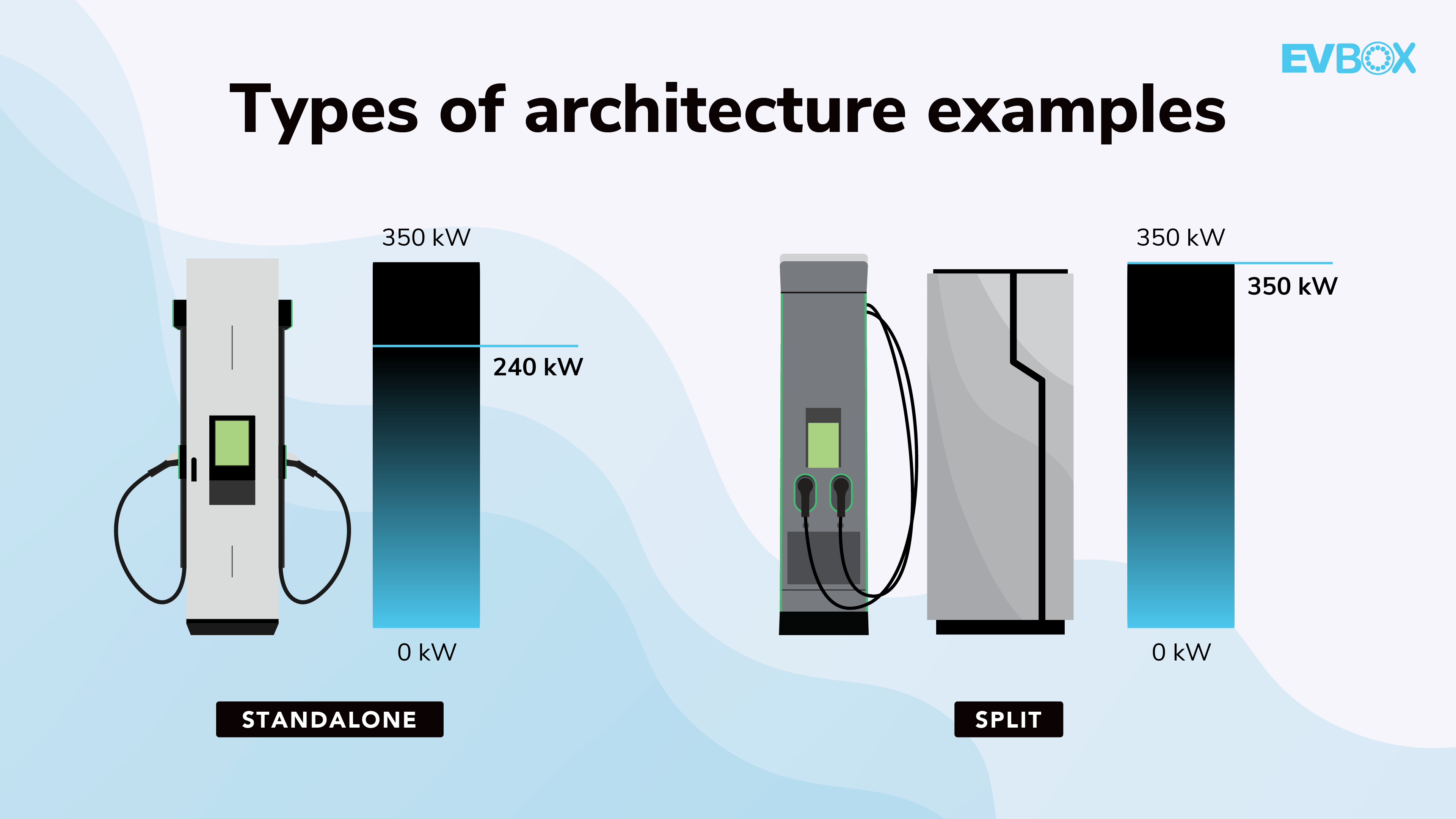
Choosing the right architecture depends on your business needs and site conditions.
Standalone DC Charging StationsÂ
Standalone units include all necessary components in one system. They are compact, easy to install, and suitable for locations where space is limited.
Split DC Charging Stations
Split systems consist of a user unit and a separate power unit. This design offers flexibility and can handle higher power outputs, but requires more space and complex installation.

Standalone vs. Split DC Charging Stations
Standalone units are ideal for on-the-go locations like highway rest stops, while split systems work well for commercial or hospitality sites requiring multiple connectors and flexibility.
DC Charging CableÂ
DC stations come with integrated cables designed to deliver maximum power efficiently. These cables are often thicker to avoid derating and may even have active cooling for high-power applications.

Maximum Power Output Isn't Always What's DeliveredÂ
Even if a station can provide 300 kW, the vehicle will only take as much as it can safely receive. For example, a Tesla Model 3 can only accept up to 250 kW, regardless of the station's capacity.
Simultaneous charging also affects the maximum output. If two cars are charged at the same time, the power is divided among them.
DC ConnectorÂ
DC fast charging connectors vary by region but are designed to handle high-power charging. Common standards include CCS in Europe and North America, Tesla’s Supercharger connector, GB/T in China, and CHAdeMO in Japan.

These connectors ensure compatibility and convenience for EV owners, supporting long-distance travel and reducing charging times.
Discover Our DC Fast Charging StationsÂ
We offer a variety of DC charging stations as part of our comprehensive EV charging solutions for businesses worldwide. Explore our portfolio of DC charging stations to find the perfect fit for your business needs.







